Wave Extensions
|SHM | Wave terms | Wave Phenomena | Extensions
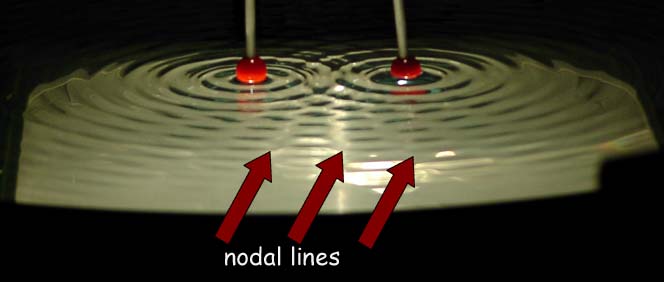
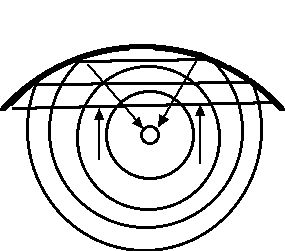
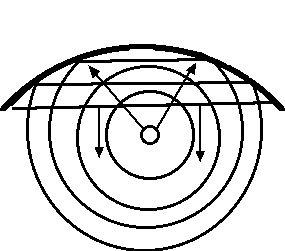
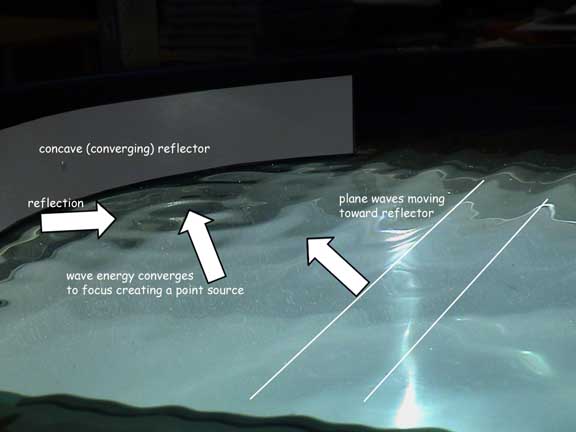
converging/diverging reflectors/refractors; standing waves
| reflectors | converging | diverging |
when wave energy is brought together as a result of reflection - the process is called converging and the energy will come together at a point called a focus.
|
when wave energy is reflected from a convex reflector it will diverge (e.g have its wave energy density decrease as the result the energy spreads out). When a plane wave reflects from a convex surface it creates a circular wave that diverges (because it seems to have originated from the focus of the concave side - acting as a virtual source because it obviously did not originate at that point). 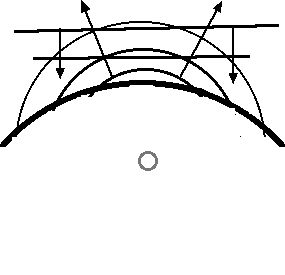 |
|
| refractor | converging | diverging |
| double convex lense | double concave lense |
Standing Waves
A cavity is created by a medium where wave energy is inserted at one end of the cavity (whose length is L). The energy propogates to the other end of the medium where its energy is reflected and refracted. The reflected energy is important because it will interfere with the incident wave. Most frequencies will create desctructive interference within the cavity. The first (lowest) frequency that constructively intferes in the cavity is called the fundamental or 1st harmonic. It is called a standing wave because its motion is not in the direction of propogation. The motion follows a simple pattern. The result is also called a resonance or a harmonic.
The end conditions of the cavity are critical to the resulting resonances. Remember that the distance between the ends of the cavity is L.
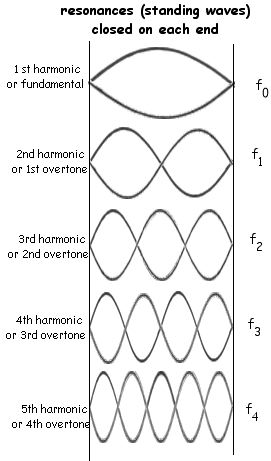 |
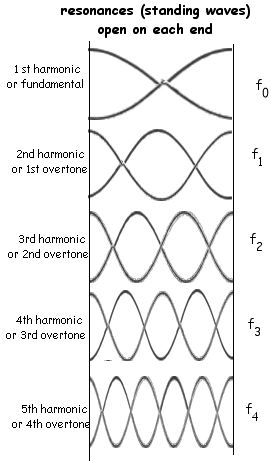 |
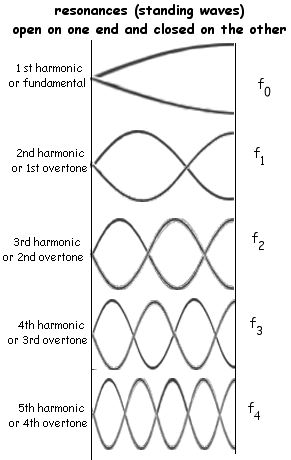 |
Young's double slit experiment: